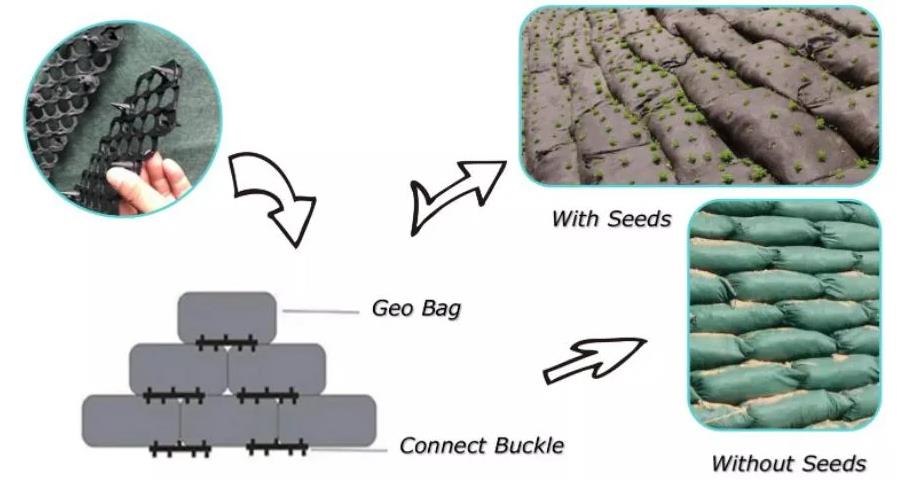
A geotextile bag, also known as a geobag or geotube, is a type of geosynthetic product used in various civil engineering and environmental applications. Geotextile bags are typically large, tubular containers made of synthetic woven or non-woven geotextile materials. These bags are filled with a specific fill material, such as sand, sludge, or other sediment, to create a containment or structural element in different projects. Here are some common uses and features of geotextile bags:

- Erosion Control: Geotextile bags are often used to control erosion in coastal areas or along riverbanks. They can be filled with sand or other materials to create a barrier against the erosive forces of water.
- Dewatering: In construction and environmental remediation projects, geotextile bags are used for dewatering sludge or sediment. The bags allow water to drain while retaining the solid particles, facilitating the separation of water from solids.
- Breakwaters and Revetments: Geotextile bags filled with sand or other materials can be used to create breakwaters or revetments, providing protection against wave action and coastal erosion.
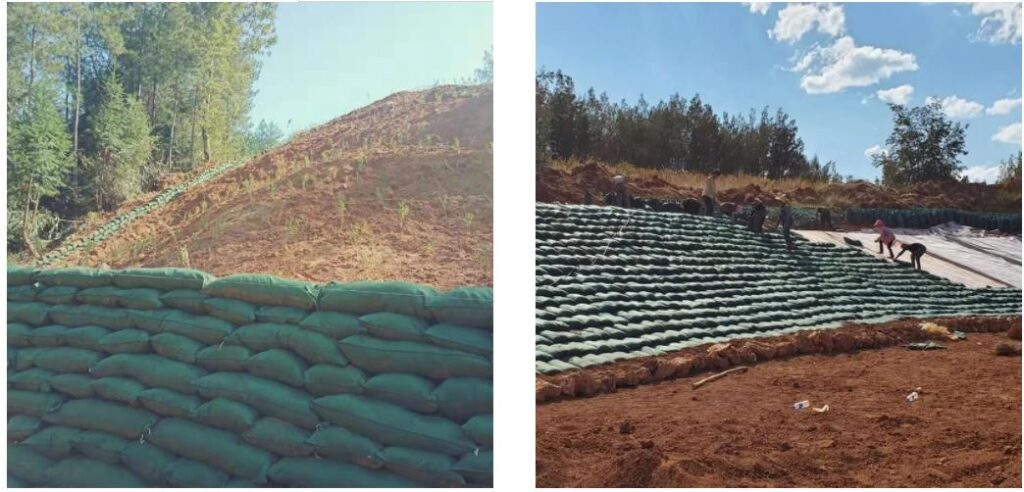
- Slope Stabilization: Geotextile bags can be employed in slope stabilization projects, helping to reinforce and stabilize slopes against the risk of landslides.
- Flood Protection: In flood-prone areas, geotextile bags filled with sand or soil can be quickly deployed to create temporary barriers for flood protection.
- Land Reclamation: Geotextile bags can be used in land reclamation projects to create new land by filling them with dredged materials or other suitable fill.
- Pipeline and Cable Protection: They can be used to protect underwater pipelines or cables by creating a protective layer around them.
- Waste Containment: Geotextile bags are used in the containment and disposal of various waste materials, providing a means to isolate and manage waste.
The choice of geotextile material, size, and fill material depends on the specific requirements of the project. Geotextile bags offer advantages such as cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and versatility in various applications. They have become a valuable tool in the field of geotechnical and environmental engineering.